Dementia
1 in 5 People Aged 65 and Older Have Dementia…

Dementia is a condition where cognitive function declines due to various causes such as brain diseases or disorders, affecting daily life.
As of 2020, it is estimated that there are approximately 6 million dementia patients aged 65 and older in Japan. By 2025, about 7 million (1 in 5 elderly individuals) are expected to develop dementia.
Even younger individuals can develop dementia due to cerebrovascular disorders or Alzheimer’s disease. Dementia that occurs before the age of 65 is called young-onset dementia, and it is estimated that there are 35,700 individuals with young-onset dementia.
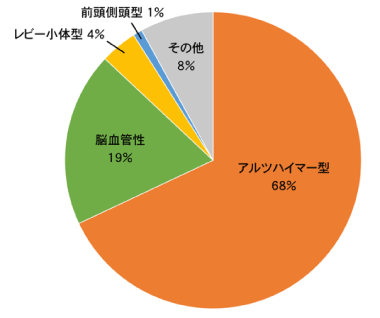
There are several types of dementia:
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
2. Vascular Dementia
3. Lewy Body Dementia
4. Frontotemporal Dementia
5. Others
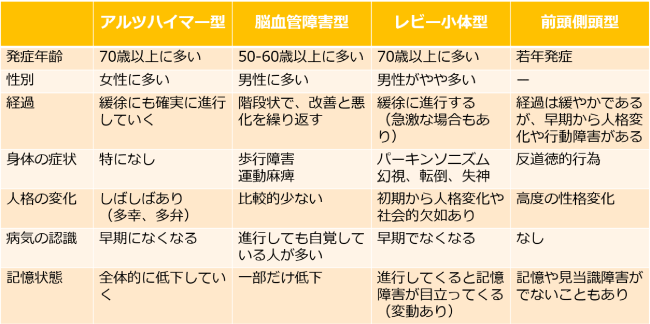
This is the most common type of dementia, caused by neurodegeneration leading to brain atrophy. Symptoms often begin with memory loss and progress gradually.
Depending on the affected brain region, symptoms may vary, often resulting in “patchy dementia,” where some cognitive functions remain intact.
The progression can be slow or sudden in a stepwise manner.
Many patients also have a combination of vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Symptoms include visual hallucinations, hand tremors, and small, shuffling steps that increase the risk of falls (Parkinsonian symptoms).
Symptoms include difficulty in speech, frequent mispronunciations, loss of emotional control, and inability to follow social rules.
Early Detection and Early Treatment
While it does not significantly interfere with daily life like dementia, a state where memory and other cognitive abilities decline but is neither completely normal nor dementia is called “Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI).” It is said that about half of people with MCI progress to dementia within five years. However, starting preventive measures such as exercise at this stage can help slow its progression.
If you feel that memory loss due to aging is becoming more noticeable, MCI may be a possibility.
– A decline in cognitive function, such as memory loss, compared to before, which is either self-recognized or noticed by family members.
– Acknowledgment of frequent memory lapses.
– No significant impairment in daily life.

Dementia symptoms can be broadly categorized into core symptoms such as memory impairment, disorientation, and reduced comprehension and judgment, and behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD).

Memory Loss (Amnesia)
⇒ Forgetting events from just minutes or hours ago.
⇒ Repeating the same questions or statements.
⇒ Frequently losing or misplacing items and always searching for them.
⇒ Forgetting appointments and purchasing the same items multiple times.
⇒ Struggling to recall the names of familiar people or objects.
Disorientation in Time and Place
⇒ Losing track of dates and days of the week.
⇒ Getting lost even on familiar routes.
⇒ Confusion about the sequence of events.
Decline in Comprehension and Judgment
⇒ Difficulty managing financial transactions.
⇒ Inability to understand situations or explanations, struggling to follow TV programs.
⇒ More frequent mistakes while driving.
Inability to Perform Work, Housework, Hobbies, or Self-Care
⇒ Making errors in cooking measurements, struggling with cleaning and laundry.
⇒ Neglecting personal grooming and failing to choose weather-appropriate clothing.
⇒ Forgetting how to wash face or bathe.
⇒ Increased food spills and incontinence.
Anxiety, fear, or loneliness when alone.
Depression, lethargy, lack of interest in hobbies or favorite TV programs.
Increased irritability, anger over trivial matters.
Hallucinations, claiming to see people who are not present.
Suspicion of theft, believing personal belongings have been stolen.
Forgetting the purpose of an outing and being unable to return home.
The Relationship Between Dementia Prevention and EMS Therapy
Cognitive abilities such as learning, memory, and recognition are influenced by a substance produced in the brain’s hippocampus called “Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF).” A decrease in BDNF levels has been linked to the progression of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and Parkinson’s disease.
In addition to the hippocampus, BDNF is also produced in muscles (skeletal muscles, which move bones). Muscle training is expected to help prevent and improve these conditions, but it requires intense physical activity, which is challenging for the elderly or ill.
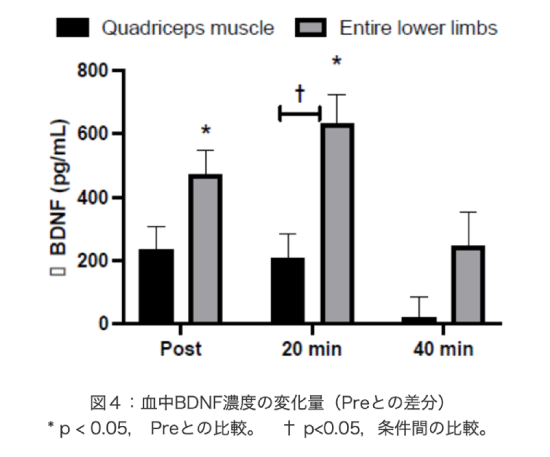
To address this, a research group from MTG, a leading technology brand, and Kanazawa University conducted an experiment on the effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (EMS) on skeletal muscles to measure BDNF levels in the blood. The results showed that the more muscles stimulated, the higher the BDNF concentration, with a significant increase sustained for approximately 20 minutes.
Especially when stimulating the gastrocnemius muscle (calf muscle), a notable effect was observed, suggesting that EMS on the calves may help prevent and improve dementia and depression in those unable to engage in physical exercise due to age or illness.
Dementia (Progression) Prevention Program
Based on the above, our company proposes and provides a combined program that includes EMS for the triceps surae (calf muscles) using ES-530 and Astron, along with acupuncture treatment aimed at increasing blood flow to the cerebral cortex and limbic system.


Although different types and stages of dementia affect different areas of the brain, brain atrophy and the presence of amyloid plaques are considered key issues. This program is also effective for those with mild cognitive impairment, often seen as a precursor to dementia, as well as for those looking to prevent dementia in the future.
Additionally, we offer the Synapsology program, which promotes brain activation.
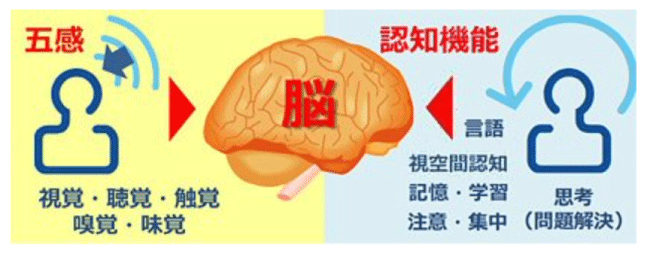
By performing movements such as “doing two things simultaneously” or “moving differently with each hand,” the program stimulates the neural network (synapses) in the brain and enhances activation. Performing these activities in a group setting increases emotional engagement, further activating the brain and contributing to improvements in cognitive and motor functions, as well as reducing anxiety.
Things to Know About Dementia Prevention